Introduction
In the complex world of construction projects, effective contract management is crucial for ensuring that projects are completed successfully, within scope, and on budget. Contracts serve as the foundation of construction agreements, outlining the terms, responsibilities, and expectations for all parties involved. Mastering contract management helps mitigate risks, avoid disputes, and ensure compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
Overview: Contract management encompasses various aspects, from drafting and negotiating terms to monitoring performance and handling disputes. It involves managing essential documents, understanding different contract types, and implementing best practices to ensure all contractual obligations are met. Effective contract management not only safeguards the interests of all stakeholders but also contributes to the smooth execution of construction projects.
In this article, we will cover:
- The key elements that are integral to effective contract management in construction.
- Different types of contracts used in construction and their implications.
- Essential documents required for robust contract management.
- Best practices to optimize contract management and prevent common pitfalls.
- The role of technology and tools in enhancing contract management efficiency.
Key Elements of Contract Management
Defining Contract Management
- Understanding the Scope and Purpose
- Key Objectives in Contract Management
Role of Contract Managers in Construction Projects
- Responsibilities and Duties
- Importance of a Contract Manager in Project Success
Contract Lifecycle Management
- Phases of the Contract Lifecycle: Initiation, Execution, and Closure
- Importance of Each Phase in Managing Contracts Effectively
Risk Management and Mitigation
- Identifying Potential Risks in Contracts
- Strategies for Managing and Mitigating Risks
Communication and Documentation
- Importance of Clear Communication in Contract Management
- Essential Documentation Practices to Maintain Transparency
Compliance and Legal Adherence
- Ensuring Contracts Meet Legal and Regulatory Standards
- Role of Compliance in Contract Management
These key elements are fundamental to understanding and executing effective contract management in construction projects, ensuring that all parties involved are aligned and that the project progresses smoothly.
Types of Contracts in Construction
Lump Sum Contracts
- Overview: Fixed price for the entire project.
- Advantages: Predictable costs, straightforward administration.
- Disadvantages: Less flexibility for changes, risk of cost overruns if scope changes.
Cost-Plus Contracts
- Overview: Contractor is paid for all project costs plus a fixed fee or percentage.
- Advantages: Flexibility for changes, transparency in costs.
- Disadvantages: Potential for cost escalation, requires detailed record-keeping.
Time and Material Contracts
- Overview: Contractor is paid based on time spent and materials used.
- Advantages: Suitable for projects with uncertain scope, allows for flexibility.
- Disadvantages: Harder to predict final costs, potential for inefficiencies.
Unit Price Contracts
- Overview: Payment is based on agreed-upon unit prices for specific tasks or materials.
- Advantages: Clarity in pricing for individual tasks, useful for repetitive work.
- Disadvantages: Requires precise measurement, potential for disputes over quantities.
Guaranteed Maximum Price (GMP) Contracts
- Overview: Sets a ceiling price for the project; any cost savings benefit the owner.
- Advantages: Owner is protected from cost overruns, encourages cost efficiency.
- Disadvantages: Requires accurate initial estimates, may lead to reduced quality if the contractor cuts corners to stay under budget.
This section covers the most common types of contracts used in construction projects, highlighting their key characteristics, benefits, and potential drawbacks. Understanding these contract types is essential for choosing the right one for a specific project, depending on the project’s scope, complexity, and risk tolerance.
Essential Documents for Contract Management
Contract Agreement
- Purpose: Defines the terms, conditions, and obligations of all parties involved.
- Key Inclusions: Project scope, payment terms, timeline, and responsibilities.
Scope of Work (SOW)
- Purpose: Provides a detailed description of the work to be performed.
- Key Inclusions: Specific tasks, deliverables, project milestones, and exclusions.
Bill of Quantities (BOQ)
- Purpose: Lists all materials, labor, and services required for the project.
- Key Inclusions: Itemized quantities, unit rates, and total costs.
Project Schedule
- Purpose: Outlines the timeline for project tasks and milestones.
- Key Inclusions: Start and end dates, critical path, dependencies, and deadlines.
Change Orders
- Purpose: Documents any alterations to the original contract.
- Key Inclusions: Description of changes, impact on cost and schedule, and approval signatures.
Payment Schedule
- Purpose: Details the timing and conditions for payments throughout the project.
- Key Inclusions: Milestones linked to payments, retainage terms, and final payment conditions.
Insurance Certificates
- Purpose: Verifies that all parties have the necessary insurance coverage.
- Key Inclusions: Types of coverage, policy numbers, and coverage limits.
Performance Bonds
- Purpose: Guarantees the completion of the project as per the contract.
- Key Inclusions: Bond amount, issuer details, and conditions under which it is payable.
Subcontractor Agreements
- Purpose: Outlines the terms between the main contractor and subcontractors.
- Key Inclusions: Scope of work, payment terms, and compliance requirements.
Inspection and Testing Reports
- Purpose: Ensures that the work meets the specified standards and quality.
- Key Inclusions: Inspection results, testing methodologies, and corrective actions.
These documents are crucial for effective contract management, ensuring that all aspects of the project are clearly defined, monitored, and executed according to the agreed terms. Proper documentation helps in avoiding disputes, managing changes, and ensuring that the project stays on track.
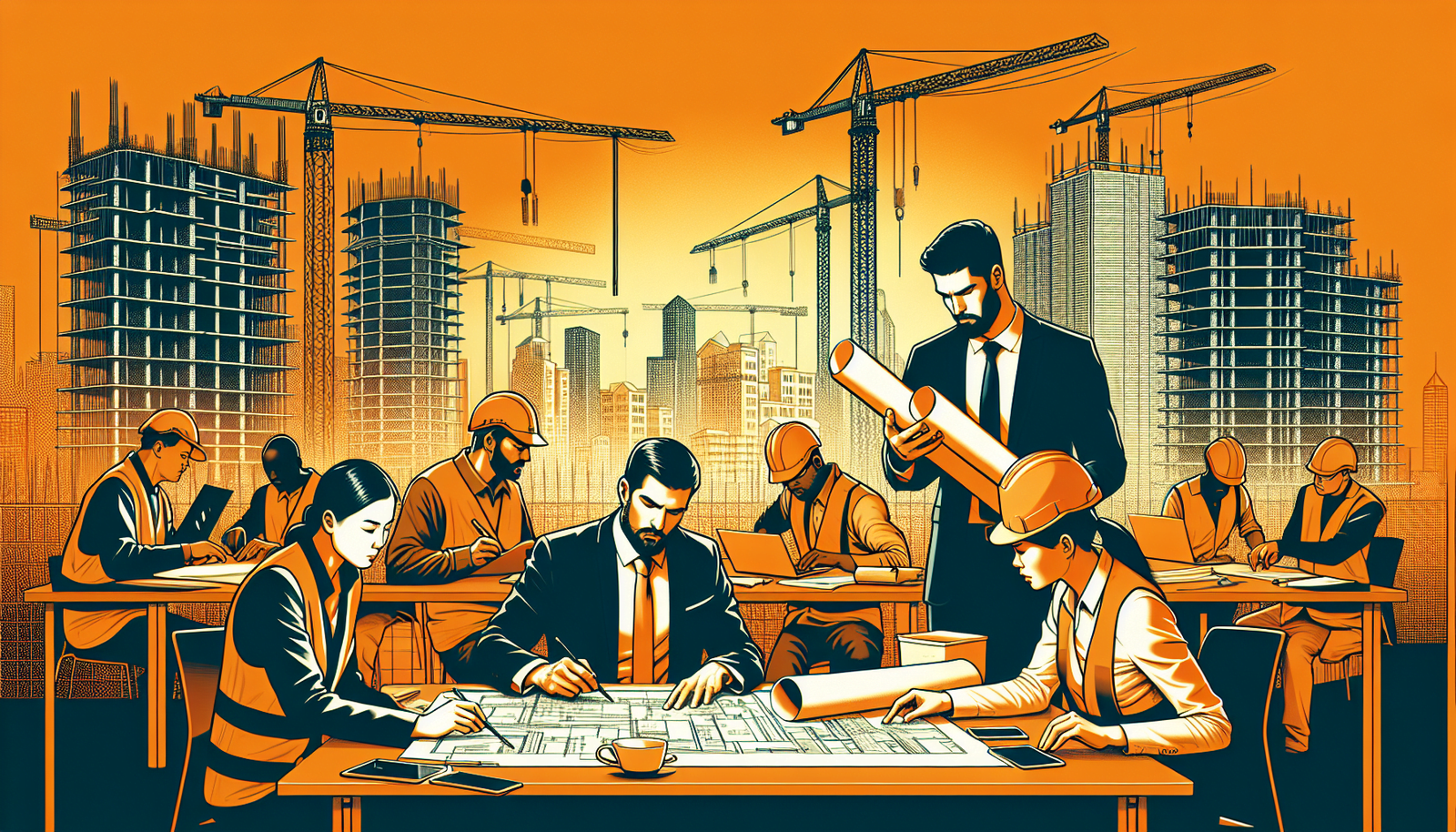

Best Practices for Effective Contract Management
Clear Communication and Documentation
- Practice: Maintain transparent and open communication among all stakeholders.
- Implementation: Regularly update project documents, and use centralized platforms for sharing information. Clearly document all decisions, changes, and agreements.
Regular Contract Review and Monitoring
- Practice: Frequently review contracts to ensure compliance and track performance.
- Implementation: Schedule periodic contract audits and use contract management software to monitor key milestones, deliverables, and deadlines.
Comprehensive Risk Management
- Practice: Identify, assess, and manage risks proactively throughout the project.
- Implementation: Develop a risk management plan that includes risk identification, mitigation strategies, and contingency plans. Regularly review and update the risk register.
Effective Change Management
- Practice: Implement a structured process for managing changes to the contract.
- Implementation: Use formal change order procedures, document all changes, and assess their impact on cost, schedule, and scope. Ensure that all changes are agreed upon and signed off by relevant parties.
Stakeholder Engagement and Collaboration
- Practice: Foster collaboration and engagement among all parties involved in the contract.
- Implementation: Hold regular meetings with stakeholders, involve them in key decisions, and ensure that their concerns are addressed promptly. Use collaboration tools to facilitate teamwork.
Use of Technology and Tools
- Practice: Leverage technology to streamline contract management processes.
- Implementation: Adopt contract management software that integrates with project management tools, enabling automation of routine tasks, document storage, and real-time updates.
Training and Development
- Practice: Invest in training for contract managers and project teams.
- Implementation: Provide ongoing training on contract management best practices, legal aspects, and software tools. Encourage knowledge sharing and continuous improvement.
Compliance and Legal Adherence
- Practice: Ensure that all contracts comply with relevant laws and regulations.
- Implementation: Work closely with legal advisors to review contracts, stay updated on regulatory changes, and ensure that all contractual obligations are met. Regularly audit compliance with contractual terms.
Performance Measurement and Reporting
- Practice: Track and measure contract performance against key metrics.
- Implementation: Establish clear performance indicators, such as cost control, schedule adherence, and quality benchmarks. Use dashboards and reports to monitor progress and make informed decisions.
Dispute Resolution Mechanisms
- Practice: Prepare for potential disputes by establishing clear resolution processes.
- Implementation: Include dispute resolution clauses in contracts, define the steps for mediation or arbitration, and ensure that all parties understand the process.
Following these best practices in contract management will help ensure that construction projects are completed on time, within budget, and to the satisfaction of all stakeholders. They provide a framework for managing contracts efficiently, minimizing risks, and handling challenges effectively.
Common Challenges in Contract Management
Scope Creep
- Challenge: Uncontrolled changes or continuous growth in project scope.
- Impact: Can lead to delays, budget overruns, and disputes.
- Solution: Implement strict change management processes, and ensure all scope changes are formally documented and approved.
Delays and Extensions
- Challenge: Unexpected delays in project timelines that affect contract obligations.
- Impact: Can lead to cost increases, penalties, and strained relationships with stakeholders.
- Solution: Regularly monitor project schedules, use buffer times, and ensure clear communication of delays and their implications.
Disputes and Conflict Resolution
- Challenge: Disagreements between parties over contract terms, performance, or interpretation.
- Impact: Can result in legal action, project delays, and increased costs.
- Solution: Include clear dispute resolution mechanisms in the contract, such as mediation or arbitration, and encourage early resolution of conflicts.
Managing Contractual Obligations
- Challenge: Ensuring all parties fulfill their contractual duties on time and according to agreed standards.
- Impact: Failure to meet obligations can result in breaches, penalties, and loss of trust.
- Solution: Use contract management software to track obligations, set reminders, and ensure timely completion of tasks.
Incomplete or Ambiguous Contracts
- Challenge: Contracts that lack detail or have vague terms can lead to misunderstandings.
- Impact: Can cause disputes, delays, and cost overruns.
- Solution: Draft contracts with clear, specific language, and ensure all parties fully understand the terms before signing.
Regulatory and Compliance Issues
- Challenge: Ensuring that contracts comply with all relevant laws, regulations, and standards.
- Impact: Non-compliance can result in legal penalties, project stoppages, and damage to reputation.
- Solution: Regularly review contracts for compliance, work with legal experts, and stay updated on regulatory changes.
Risk Management
- Challenge: Identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks throughout the contract lifecycle.
- Impact: Unmanaged risks can lead to project failure, financial loss, and contractual disputes.
- Solution: Develop a comprehensive risk management plan, and regularly update it based on project progress and new information.
Communication Breakdown
- Challenge: Poor communication between stakeholders can lead to misunderstandings and misaligned expectations.
- Impact: Can cause project delays, quality issues, and disputes.
- Solution: Establish clear communication channels, hold regular meetings, and document all key decisions and changes.
Cost Overruns
- Challenge: Exceeding the budget due to inaccurate cost estimates, unforeseen expenses, or poor financial management.
- Impact: Can lead to project delays, financial strain, and disputes over who bears the extra costs.
- Solution: Implement rigorous cost control measures, regularly review budgets, and include contingency plans in the contract.
Technology Integration
- Challenge: Difficulty in integrating contract management tools with other project management systems.
- Impact: Can result in data silos, inefficiencies, and errors.
- Solution: Choose contract management software that integrates well with existing tools, and provide training to ensure smooth adoption.
By recognizing and addressing these common challenges in contract management, construction professionals can better navigate the complexities of their projects, leading to more successful outcomes and stronger stakeholder relationships.
Technology and Tools for Contract Management
Contract Management Software
- Overview: Dedicated software designed to manage the entire contract lifecycle, from creation and negotiation to execution and renewal.
- Key Features:
- Centralized contract repository for easy access and storage.
- Automated reminders for key dates, such as renewal or expiration.
- Customizable templates for consistent contract creation.
- Reporting and analytics tools to monitor contract performance.
- Popular Tools:
- Procore: Comprehensive construction management platform with contract management capabilities.
- ContractWorks: Simple, secure, and cost-effective contract management software.
Project Management Tools with Contract Integration
- Overview: Project management platforms that integrate contract management functionalities, allowing for seamless coordination between project tasks and contractual obligations.
- Key Features:
- Task tracking aligned with contract milestones.
- Collaboration features for managing contract-related communications.
- Financial management tools to track budgets and costs linked to contracts.
- Popular Tools:
- Asana: Project management software with features for tracking contract-related tasks.
- Smartsheet: Offers contract management templates within its versatile project management platform.
Document Management Systems (DMS)
- Overview: Systems designed to store, manage, and track documents electronically, crucial for maintaining contract records and associated documentation.
- Key Features:
- Version control to track changes and maintain contract integrity.
- Secure access controls to protect sensitive contract information.
- Search and retrieval capabilities for quick access to specific contract documents.
- Popular Tools:
- SharePoint: Microsoft’s platform for document management and collaboration.
- DocuSign: Not only for e-signatures but also provides a robust platform for managing contract documents.
E-Signature Tools
- Overview: Tools that enable the electronic signing of contracts, streamlining the approval process and ensuring contracts are signed quickly and securely.
- Key Features:
- Legal compliance with electronic signature laws.
- Audit trails to track the signing process.
- Integration with contract management and document management systems.
- Popular Tools:
- DocuSign: Industry-leading e-signature tool that integrates with many contract management systems.
- Adobe Sign: Another top e-signature solution with broad integration capabilities.
Risk Management Tools
- Overview: Tools specifically designed to identify, assess, and mitigate risks within contracts, helping to safeguard against potential project pitfalls.
- Key Features:
- Risk assessment templates tailored to contract management.
- Scenario analysis to predict the impact of contract changes or potential risks.
- Reporting tools to keep stakeholders informed about risk status.
- Popular Tools:
- RiskWatch: Comprehensive tool for assessing and managing risk within contracts.
- Resolver: Offers risk management solutions that can be customized for contract management.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning Tools
- Overview: Advanced tools that utilize AI to enhance contract management processes, such as contract analysis, compliance checks, and predictive analytics.
- Key Features:
- AI-powered contract review and analysis to identify potential risks or errors.
- Automated contract drafting using AI to reduce manual effort and errors.
- Predictive analytics to forecast outcomes based on historical data.
- Popular Tools:
- Kira Systems: AI-powered contract analysis and review tool.
- Luminance: Uses AI to assist in contract review, due diligence, and risk assessment.
Collaboration and Communication Platforms
- Overview: Tools that facilitate real-time collaboration and communication among contract stakeholders, ensuring that all parties are aligned and informed.
- Key Features:
- Real-time chat and discussion forums for contract negotiations and updates.
- Document sharing and collaboration features to work on contract drafts.
- Integration with other contract management and project management tools.
- Popular Tools:
- Slack: Widely used collaboration tool that integrates with many contract management systems.
- Microsoft Teams: Offers robust communication features and integrates with SharePoint for document management.
Compliance and Legal Tools
- Overview: Tools that help ensure contracts meet all legal and regulatory requirements, reducing the risk of non-compliance.
- Key Features:
- Legal clause libraries for quick access to standard legal language.
- Compliance checklists to ensure all necessary legal requirements are met.
- Automated alerts for regulatory changes that may impact contracts.
- Popular Tools:
- Thomson Reuters Legal Tracker: Comprehensive legal management software with contract compliance features.
- ContractSafe: Focuses on contract management with strong compliance tracking capabilities.
Implementing the right technology and tools for contract management can greatly enhance efficiency, accuracy, and compliance in construction projects. These tools streamline processes, reduce risks, and ensure that contracts are managed effectively from start to finish.
Legal Considerations in Construction Contracts
Understanding Contractual Terms and Conditions
- Key Terms: Definitions, scope of work, and performance standards.
- Importance: Ensures all parties have a clear understanding of their obligations and expectations.
- Best Practices: Thoroughly review and clarify any ambiguous terms before signing.
Compliance with Local and National Regulations
- Building Codes and Standards: Adherence to local, state, and national construction codes and standards.
- Permits and Licenses: Ensuring all necessary permits and licenses are obtained and maintained.
- Best Practices: Consult with legal experts to stay updated on relevant regulations and ensure compliance.
Risk Allocation and Liability
- Risk Allocation: Defining how risks are shared between parties, including responsibility for delays, cost overruns, and unforeseen conditions.
- Liability Clauses: Determining who is liable for damages or failures to meet contractual obligations.
- Best Practices: Clearly outline risk allocation in the contract and include provisions for indemnity and insurance.
Dispute Resolution Mechanisms
- Methods: Arbitration, mediation, and litigation options for resolving disputes.
- Process: Procedures for initiating and managing dispute resolution processes.
- Best Practices: Include clear dispute resolution clauses in the contract to prevent conflicts from escalating and ensure a fair resolution process.
Change Management and Variations
- Change Orders: Procedures for handling changes to the project scope, schedule, or cost.
- Variations: Managing variations in work and adjusting the contract accordingly.
- Best Practices: Implement formal change order processes and document all changes to avoid disputes and ensure transparency.
Contract Termination Clauses
- Termination Conditions: Conditions under which the contract can be terminated by either party.
- Consequences: Provisions for handling the consequences of contract termination, including compensation and the settlement of outstanding obligations.
- Best Practices: Define termination rights and procedures clearly to manage potential disputes and ensure a smooth transition if termination occurs.
Force Majeure Clauses
- Definition: Clauses that address unforeseen events that prevent parties from fulfilling their contractual obligations, such as natural disasters or political unrest.
- Impact: Specifies how such events affect the contract and the responsibilities of each party.
- Best Practices: Include a comprehensive force majeure clause to protect against extraordinary events and outline the procedures for handling such situations.
Insurance and Bonding Requirements
- Types of Insurance: Liability insurance, performance bonds, and builder’s risk insurance.
- Coverage Requirements: Ensuring adequate coverage to protect against potential risks and liabilities.
- Best Practices: Verify that all insurance and bonding requirements are met and documented in the contract to mitigate risks and ensure financial protection.
Contractual Obligations and Enforcement
- Obligations: Ensuring all parties meet their contractual obligations, including deadlines, quality standards, and payment terms.
- Enforcement: Mechanisms for enforcing contractual terms and addressing breaches.
- Best Practices: Regularly review contractual obligations and maintain records of compliance and performance to support enforcement if necessary.
Intellectual Property and Confidentiality
- Intellectual Property Rights: Ownership and usage rights for any intellectual property created during the project.
- Confidentiality Agreements: Protecting sensitive information shared between parties.
- Best Practices: Clearly define intellectual property rights and confidentiality terms in the contract to protect proprietary information and avoid disputes.
Addressing these legal considerations in construction contracts helps ensure that all parties understand their rights and responsibilities, reducing the likelihood of disputes and enhancing project success. Properly drafted contracts that account for these factors provide a solid foundation for effective project management and legal protection.
Case Studies and Examples
1. Case Study: Complex Change Orders in a High-Rise Construction Project
- Project: Urban high-rise residential building.
- Issue: Frequent and extensive change orders due to evolving client requirements and unforeseen site conditions.
- Resolution: Implemented a formal change order process with detailed documentation and approval protocols. Used project management software to track changes and manage impacts on cost and schedule.
- Outcome: Improved transparency and control over change orders, resulting in reduced disputes and more accurate project forecasting.
2. Case Study: Dispute Resolution in a Commercial Office Renovation
- Project: Renovation of a commercial office space.
- Issue: Dispute arose over delays in the completion of electrical work, leading to project delays and cost overruns.
- Resolution: Contract included a dispute resolution clause specifying mediation followed by arbitration. The parties engaged in mediation to reach a settlement before escalating to arbitration.
- Outcome: Effective dispute resolution process minimized the impact of delays and cost overruns, leading to a successful project completion.
3. Case Study: Managing Scope Creep in a Residential Construction Project
- Project: Custom home construction.
- Issue: Client requests for additional features and design changes led to scope creep and increased project costs.
- Resolution: Established a change management process requiring formal change orders for any additional work. Clearly defined scope and pricing terms in the contract.
- Outcome: Reduced scope creep and controlled additional costs, ensuring the project stayed within the agreed budget and timeline.
4. Case Study: Compliance Challenges in an Infrastructure Project
- Project: Highway expansion project.
- Issue: Project faced compliance challenges with evolving environmental regulations.
- Resolution: Engaged legal experts to ensure all contract terms met regulatory requirements and updated contract documents to reflect new compliance standards.
- Outcome: Successful navigation of regulatory changes without project delays, maintaining compliance and avoiding legal penalties.
5. Case Study: Risk Allocation in a Large-Scale Industrial Facility
- Project: Construction of an industrial manufacturing facility.
- Issue: High risk of cost overruns and delays due to complex project requirements and site conditions.
- Resolution: Allocated specific risks to relevant parties through detailed contract clauses. Included performance bonds and insurance to mitigate potential risks.
- Outcome: Effective risk management led to successful project completion within budget and timeline, with minimized financial exposure for all parties.
6. Case Study: Use of E-Signature Tools in a Fast-Paced Construction Project
- Project: Fast-tracked commercial building renovation.
- Issue: Need for rapid contract approvals and execution to meet tight deadlines.
- Resolution: Implemented e-signature tools to streamline the contract approval process. Integrated with contract management software for efficient document handling.
- Outcome: Accelerated contract execution and approvals, contributing to the timely completion of the renovation project.
7. Case Study: Insurance and Bonding Requirements in a Government Project
- Project: Construction of a government-funded community center.
- Issue: Stringent insurance and bonding requirements to ensure project completion and protect against potential risks.
- Resolution: Met all insurance and bonding requirements as specified in the contract. Provided proof of coverage and compliance to the project owner.
- Outcome: Fulfilled all contractual insurance and bonding obligations, providing assurance to the project owner and facilitating smooth project execution.
8. Case Study: Confidentiality Agreements in a Technology Facility Construction
- Project: Construction of a high-tech data center.
- Issue: Need to protect sensitive information related to technology infrastructure and proprietary systems.
- Resolution: Included strict confidentiality clauses in the contract to safeguard sensitive information. Implemented access controls and non-disclosure agreements with all contractors.
- Outcome: Successfully protected proprietary information and technology details, ensuring confidentiality throughout the project.
These case studies and examples illustrate various scenarios and solutions related to contract management in construction projects. They highlight the importance of clear contractual terms, effective risk management, and the use of technology to address common challenges and ensure successful project outcomes.
Conclusion
Effective contract management is crucial to the success of construction projects, ensuring that all parties fulfill their obligations and that projects are completed on time and within budget. By understanding and addressing legal considerations, such as scope creep, compliance, and risk allocation, construction professionals can navigate the complexities of contract management more efficiently.
Summary of Top Free Software Options:
- Procore: A comprehensive tool for managing contracts and project documentation.
- ContractWorks: Offers essential contract management features with a focus on simplicity.
- Asana: Integrates project management tasks with contract management functionalities.
- Smartsheet: Provides customizable templates and tracking for contracts and project management.
- DocuSign: Leading e-signature solution for efficient contract execution.
- SharePoint: A robust document management system with collaborative features.
- Adobe Sign: Another top choice for electronic signatures and document handling.
- RiskWatch: Specializes in assessing and managing risks associated with contracts.
- Luminance: Uses AI for contract review and risk assessment.
- Slack: Facilitates real-time communication and collaboration related to contracts.
Final Recommendations for Small Businesses:
For small businesses, selecting the right free or cost-effective tools is key to managing contracts effectively without straining resources. Prioritize software that offers essential functionalities like document storage, change management, and e-signatures. Focus on tools that integrate well with your existing systems and offer scalability as your business grows. Invest time in understanding each tool’s capabilities and choose those that align with your specific needs.
By leveraging these tools and adhering to best practices in contract management, you can improve efficiency, reduce risks, and ensure smoother project execution. Regularly reviewing and updating your contract management processes will help maintain control and foster successful project outcomes.






Leave a Reply